Ok, so you are ready to update your website pages, or these days, a web-based app page. Well planning content is critical for making the most of your site pages. Here are several tips that should be included in refining a site or app page.
Finally, remember to optimize for search engines - i.e. use SEO to rank your site in a search query. Without this, your website has not guidance for search or even for a paid search marketing plan.
The most critical mistake with websites is to make delays to deliver your content to a developer or designer – more than a few months to code and finalize function can be problematic for your designer to organize and revise code with quality. Those delays can also cost your business sales, because your business’ updating of a site reflects how well it is operating. Gather essential changes so you can share your concerns upfront, and make any changes in an organized fashion.
With analytics deployment these days, cross device measurement has become a de facto standard for establishing effective measurement for many businesses. It allows marketers to learn if customers are viewing a tagged site on a mobile device and website prior to a conversion. This information can help tailor plans for a customer experience.
One essential tool in establishing cross device measurement is a JavaScript-oriented call out called User ID. A number of analytic tools, such as Google Analytics and Piwik offer this feature. The following tips focuses on the well-known Google Analytics platform.
User ID is a modification to the analytics tag, designed to allow cross device visits to be an identifiable segment in the analytics reports. User ID is one of two IDs that vary according the data source generating the data. A client ID represents a device or access by browser, while a user ID represents a signed in user with an account. The purpose behind both IDs is to avoid personal identifiable information from appearing in the Google Analytics reports or within an overall analytic stack where Google Analytics data is exported.
For Google Analytics, User ID must first be enabled in an account, then added as a modification in the site tracking code. (To learn more about User ID see this CMSWire post)
To enable the User ID, enter the admin of the desired account and navigate to the property level. Within the Property level column, click Tracking Info then User ID. You will then see the following step by step instructions:
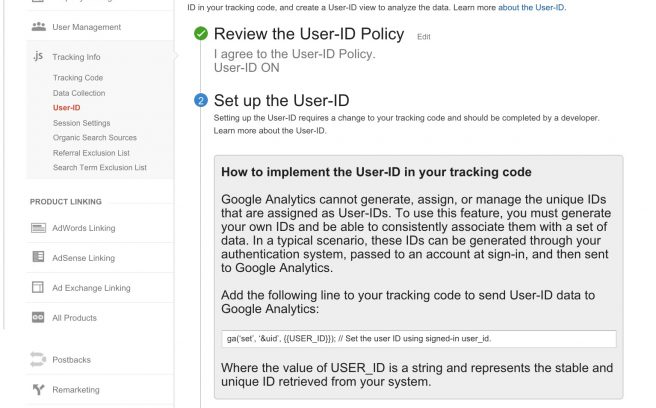
The first step is an explanation of the User ID Policy - the wording is meant to explain what is considered personally identifiable information and avoid its usage when marketers create the User ID. Once read, you can indicate you understand the User ID Policy by toggling the switch to ON. The feature is then enabled in the selected analytics account.
The next step, which appears right after activation, is to generate an unique ID that associates to new users and that consistently reassign IDs to returning users. These IDs are included in the data sent to Google Analytics. Ensuring these objectives does require some familiarity with JavaScript, since the variables and data type syntax is JavaScript based. Thus creating the syntax for the ID is best completed by a developer.
User ID can be used for both websites and mobile apps. Web data can only be sent to a web property, and mobile app data can only be sent to an app property, so you can not combine them into one reporting view.
The Google Tag Manager has a slightly different take on the instruction to add the User ID tag. Marketers are still required to indicate that personally identifiable information will not be used in creating the User ID. The difference lies in setting a JavaScript variable.
The tag manager variable can retrieve the User ID value from two formats. It can retrieve the value from a first party cookie which persists a user ID on the client side, or through a data layer variable.
In the Tag Manager account, navigate to the More settings, then to the Fields to Set option and click Add Field. You should see the following selection.
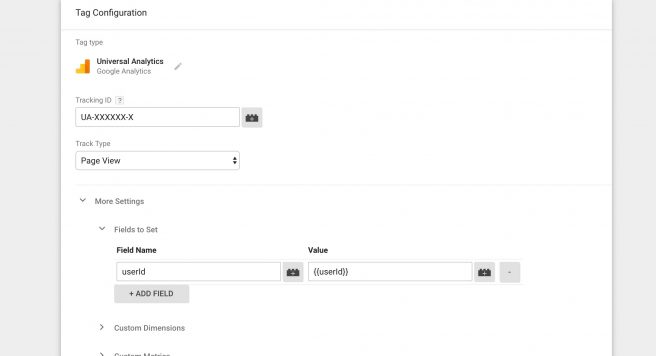
Notice the field name and value entry windows. This is where you can enter the following values.
| Field Name |
Value
|
|---|---|
|
userId
|
{{userId}}
|
Fake content is in the news these days, thanks to accusations by the Trump administration - which itself offered positions to Breitbart, an alt-right site accused of posting misogynistic, racist, and often false news.
Avoiding fake sites has been critical ever since commercial interest arrived on the web. It can appear in many technical aspects of a website. Link building was meant to signal to search engines that a site with a large number of links represented a quality source of material that should rank highly in a query.
But now, thanks to social media and user’s overlook in reviewing details of the post they share, it is very easy to spread and repeat information that is not entirely true.
Businesses and marketers of all levels have to be accountable. Sharing links to nefarious sites damages trust and branding. It can also lead to legal issue
Here are some ways to protect your sites from association with a fake or susceptible site.
So when is it a good time to replace a website?
It’s an honest question. A website is a business presence, and when your website does not work, you and your business don’t work. ultimately you do some research on your competitors in order to stay at par or better yet one step ahead.
But there are a number of significant clues to obsolesce that you should discern from your analytic metrics about your own site. Here’s the key questions to ask:
That second point raises the most serious concern, because navigation is related to the amount of information that the site is meant to convey. Are people navigating a lot to get to the information they want? Are they scrolling a long page without a large image to draw an eye -- this layout is a 1990s ploy incompatible of tablets and mobile phone, and deployment of internet access through carriers.
It also reflects a lot of information is being conveyed - it means you have a lot of clutter. This Zimana post explains why your site should not be cluttered.
Ultimately you must realize that the world of online solutions is constantly changing. If your site was built when Explorer 6 was all the rage, then this is the year for a redesign…Sites are being designed much differently now than they were even a few years back. Plus search engines have systematically revised algorithms and criteria for ranking sites in queries. It’s probably a good idea to re-design every few years to stay up to date and ensure the site shows how your business benefits customers.
Some simple fixes to consider for a meaningful updating:
And there are other ideas you can use to to improve a website - check out this list of idea. You can also examine these posts for further refinement:
E-commerce has become an essential component to retail, but it also can introduce a number of missteps to allow a customer to make a sale. These 5 tips highlight the flaws that can appear (and some tips in avoiding them with e-commerce analytics).
1. Making online activities difficult for the customer to complete.
E-commerce sites can get a bit complicated when tasked to carry a multitude of products. Any commerce site will require some adjustment to ensure that customers can complete purchase easily.
Thus a key analysis is to examine the visitor flow reports to determine which pages keep the purchasing behavior simple. Highlight where visitors are exiting a page, and examine the content on that page for improvement ideas.
Page speed can also be examined, to determine if images or scripts are creating page load issues. Slowly loading pages can persuade visitors to leave a site. Page load service Yottaa discovered in its analysis that a 1 second delay in page load speed can lead to a 7% decline in conversion, which means lower sales. Check out this Zimana post for more on page load tools and this post on tips to improve page speed for e-commerce.
2. Not targeting the right customers
To attract the right customer to the site, use the Demographic reports in Google Analytics to monitor how site traffic best matches the intended audience. The age group reported should reflect the expected customer base. For example, a music site offering downloads should reflect younger customers if the bulk of its music sales are the hottest acts that appeals to teens and younger adults.
3. Advertising that eats into low margin products
Selling low margin products online does not eliminate the risk of selling at a loss. If those items require paid search to be highlighted, then the advertising costs can exceed the margins from each sale. For example, if an AdWords campaign costing $2-$3 a click exceeds a $1 margin of an advertised product, then a retailer is spending more than what it makes on that product.
Periodically analyze the average order value of each purchase, and examine sales by SKU. Is there a better way to offer the product - by advertising a low margin product as part of a package rather than as a solo purchase.
Moreover, analyze conversions from AdWords campaigns - are the click throughs leading to sales? Use Smart Goals to help plan the identify visits that are “most likely” to convert.
Follow up with bidding alerts in the AdWords manager to stop campaigns when bid cost exceed a planned amount.
4. Not carrying what customers are looking for.
Using the site search reports can highlight the terms in which customers are constantly looking for. The terms will likely be brands or products not offered. Frequent appearance of such terms indicate potential interest; Time after search metrics can indicate if people are remaining on-site after a search, or leaving immediately after a query, implying a dissatisfaction and that the item should have been offered on the site.
This CMS wire post can explain more about how site search reports can be best analyzed.
5. Annoying your customers with hidden costs.
No customer like surprise details about a transaction when they shop online, so a good e-commerce site should highlight complete purchase information at the check out stage. A product page should set expectations of what the customer will expect when purchasing.
Monitoring the check out metrics in the commerce report can provide an indication if customers are consistently leaving the check out process. There are two steps that can address traffic decline.
One way is to set up a survey to trigger at the shopping cart when the customer drops out of the cycle.
Another way is setting up an A/B test to compare content can highlight what images or descriptions better resonate with customers.
Let me set the scene for when you receive pitches for SEO.
It’s late at your office or maybe an early morning quick check of things to do. You fire up the tableland take a last minute review of email. An unsolicited note catches your eye, with a message like this:
Hi, my name is Terrance and I am the sales manager at Such-n-such SEO and Extraordinary Marketing services. I was just looking at your site and see that your site has the potential to get even more visitors. I just want to take the time to tell you how. Now, let me ask you…
Ok, stop. It is at this point you should put the note aside, and start onto other pressing business.
Because accepting to do business from a SEO firm that starts with one blind suggestion is a waste of time. Here’s why….
Results from one specific SEO suggestion cannot guarantee traffic or a significant improvement in performance. The most complete SEO involves a combination of steps addressing page text, links, social sharing, and supporting code in a site layout will ultimately attract the right search engine queries from the right customers. To make such a combination valuable to the client, a SEO firm needs to review objectives with the website owner. That means understanding the business as much as understanding the website.
Thus when approached with a cold call about SEO, you may be receiving word on a needed task such as revising metadata or updating links. But most times cold calling SEO firms approach potential customers with an obvious site tasks so that the salesperson can just get a foot in the door. And many times, that foot is an unwelcomed one, selling unnecessary services or consuming precious time with poor follow up.
Most sites require an update over time. To ensure that the it’s up to YOU, THE CUSTOMER to determine what and when that update is put into place.
Now, here’s what your business can do to manage cold calls.
Overall, remember that a SEO firm can gain some information from your site code to ask a seemingly relevant question, but don’t work with firms that have not proven their value to other businesses and people.